
Cordlife Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT)
With just a simple blood test as early as 10 weeks into pregnancy.
Enrolling for Cordlife NIPT
Cordlife NIPT must be prescribed by your obstetrician who will explain the details about NIPT to ensure the test is suitable for you.
Cordlife NIPT gives you an accurate insight into your developing baby’s health.

*Based on the comparison of sensitivity performance of various service providers with published results.
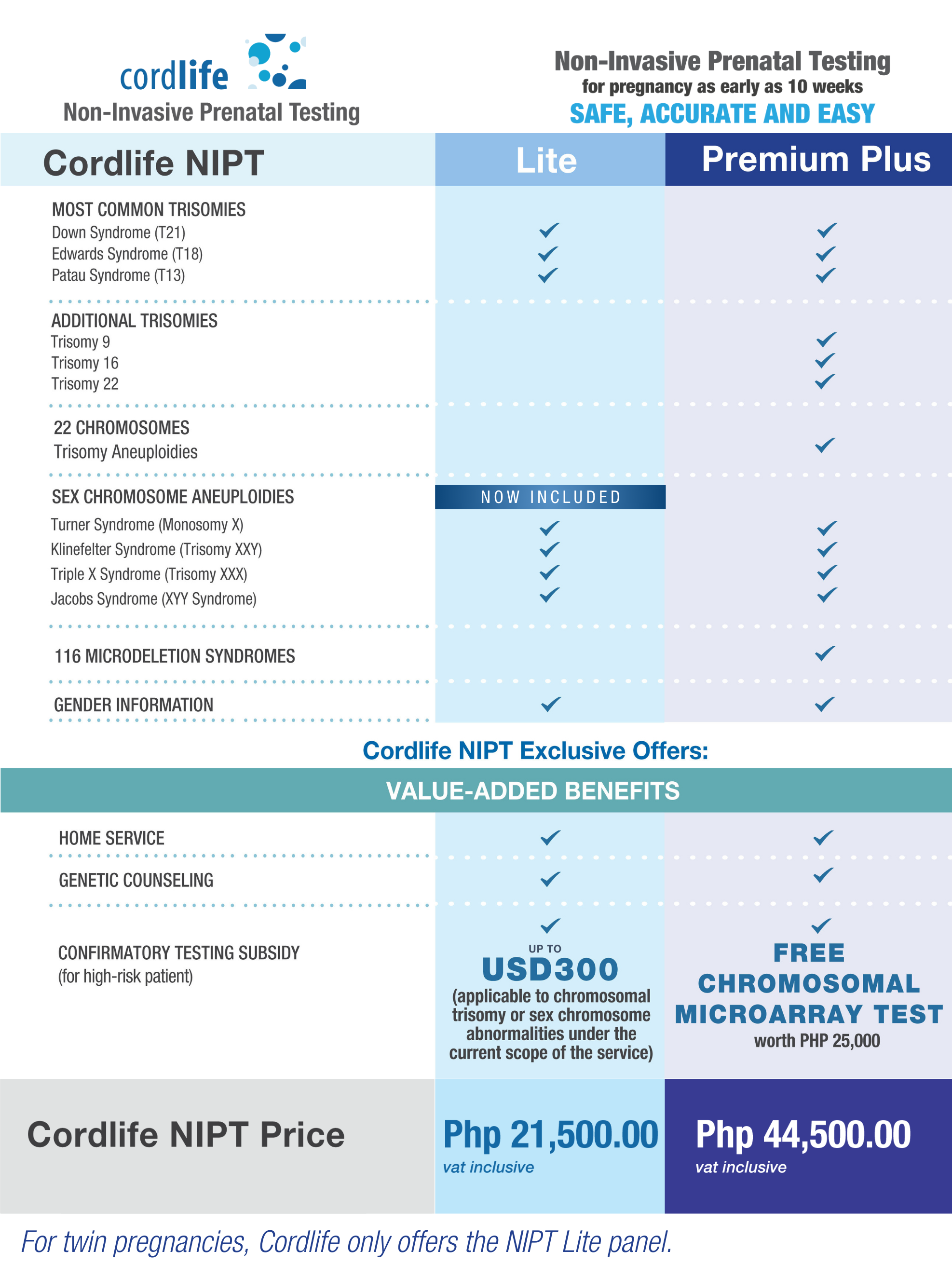
Choose What's Best For You
How do I enroll for NIPT?

Step 1
Inquire with your Obstetrician about Cordlife NIPT, send us an email at ph.info@cordlife.com, or visit our website at biotech.cordlife.ph/nipt-inquiry to schedule an appointment for the test.

Step 2
Simple blood test will be performed on you, with the option to do it in the convenience of your own home.

Step 3
After 7-10 working days, receive a detailed report through your doctor.

Get to know your baby a little bit better.
Every parent dreams of a healthy future for their baby. With Cordlife NIPT, you can prepare for your baby’s journey with confidence. Our non-invasive test ensures you get the answers you need, safely and simply.




